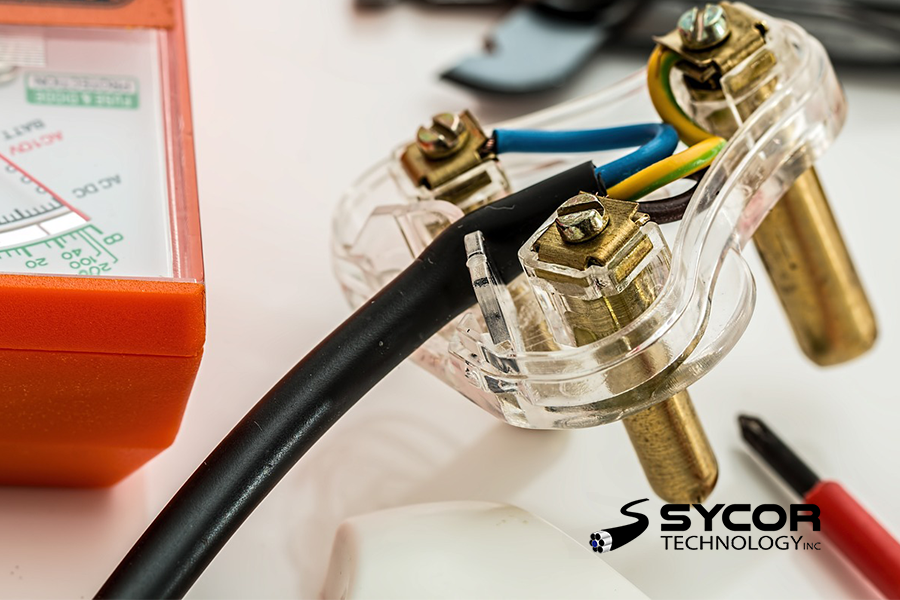

Four custom cabling parts that could make or break your application:
1. Conductor
Choosing the correct conductor is the first important consideration. An electrical conductor can come in tinned, nickel, silver, aluminum and bare copper. Although bare copper is typically the most used, each material type has unique characteristics that help applications in different ways.
1.1 Silver: is the most conductive, but also the most expensive. With the price so high, there are only a few applications that can significantly benefit off this material.
1.2 Nickel: is a reliable choice for operating at high and low-temperatures. It also has the ability to continually operate in applications that are subject to environmental influences like acids, water and leaching.
1.3 Aluminum: conductors are known for their lightweight and cheap cost. Aluminum is also one of the least conductive materials, which is why conductors are typically much larger than any other type.
1.4 Copper: is the most used conductor because of its low thermal expansion, low price and high conductivity.
1.5 Tinned: conductors are the easiest material to soldier, which makes custom cables and cable assemblies much easier to install. Moderate conducting ability.
1.6 Stranding
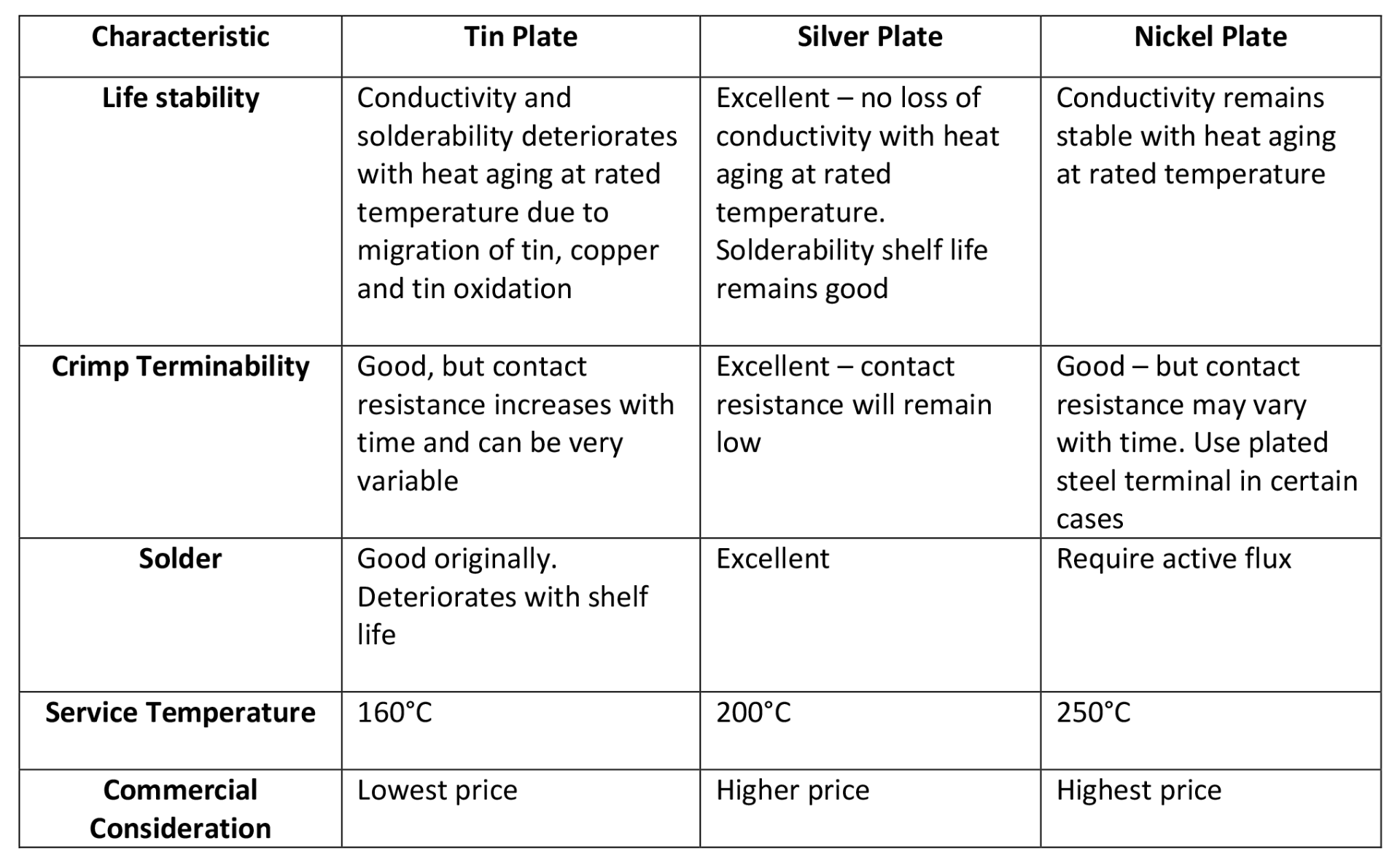
Standing is a factor that is often overlooked, but is still important when creating custom cables. The different custom cable stranding are:
Bunch: When the conductors' strands are twisted together with no arrangement.
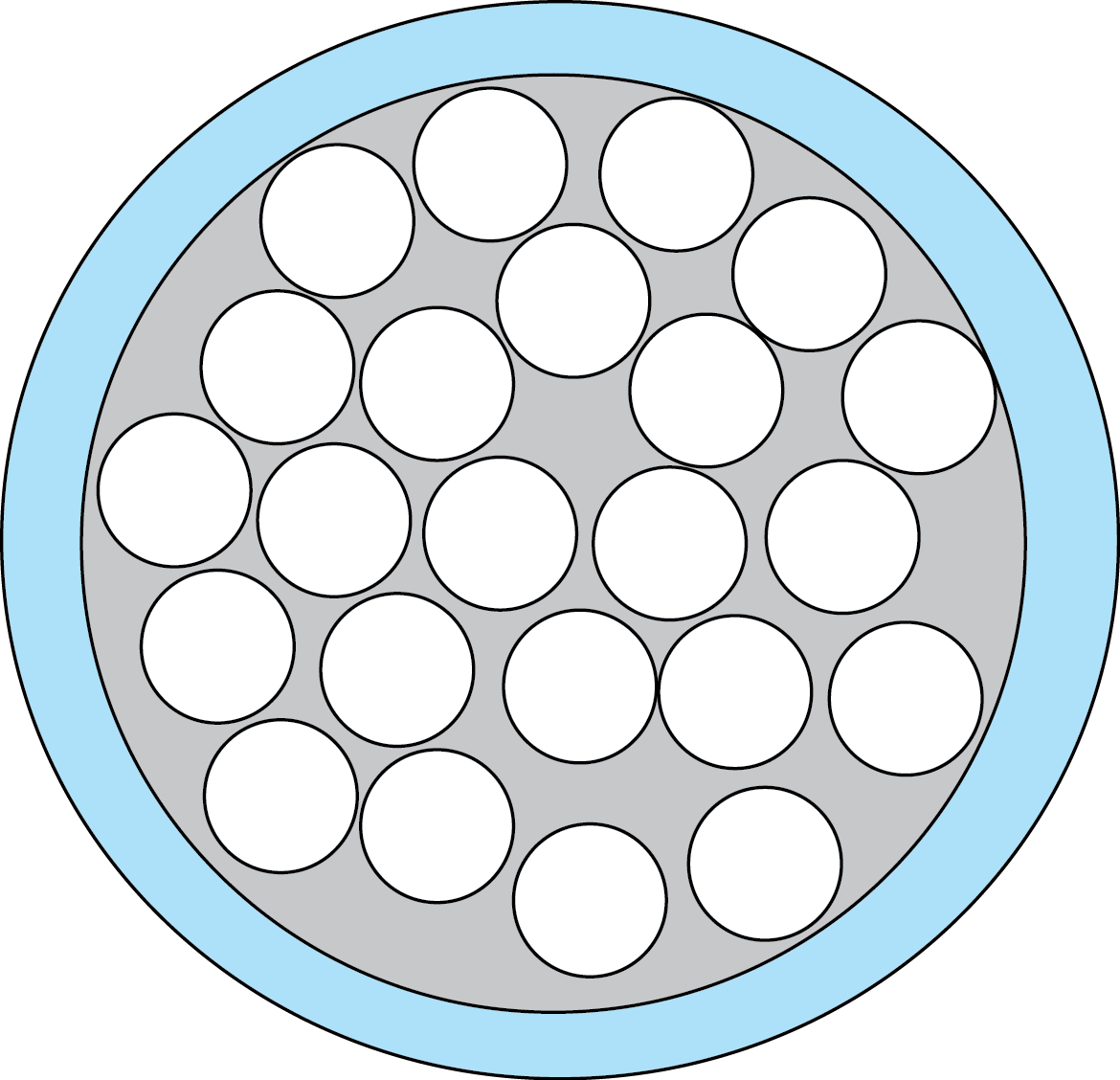
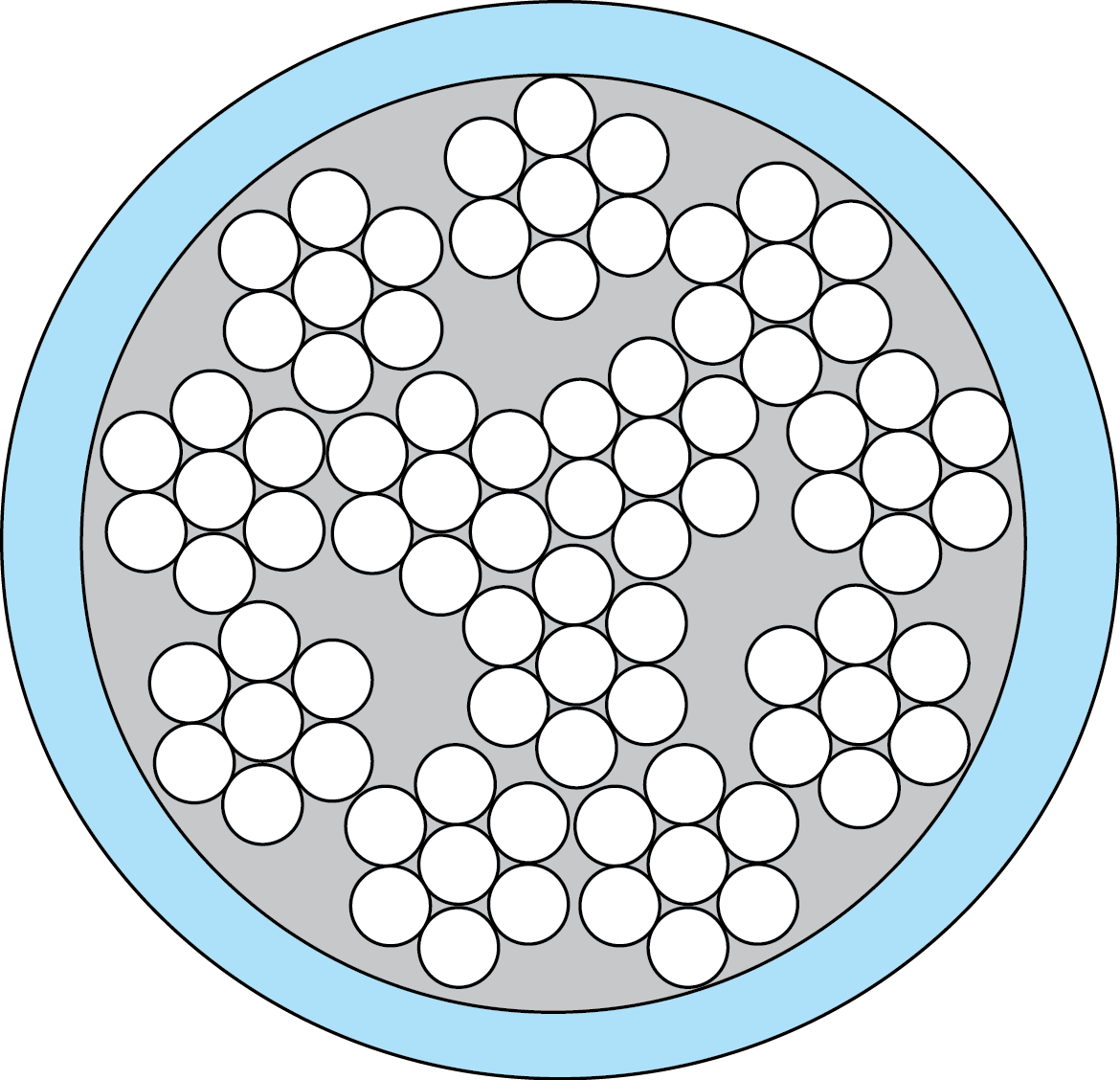
Concentric: is when a central wire is surrounded by another layer of wires and that layer is then surrounded by the following layer. Unlike other standing types once one layer is placed the following layer will often twist the opposite direction with six more wires than the previous layer.
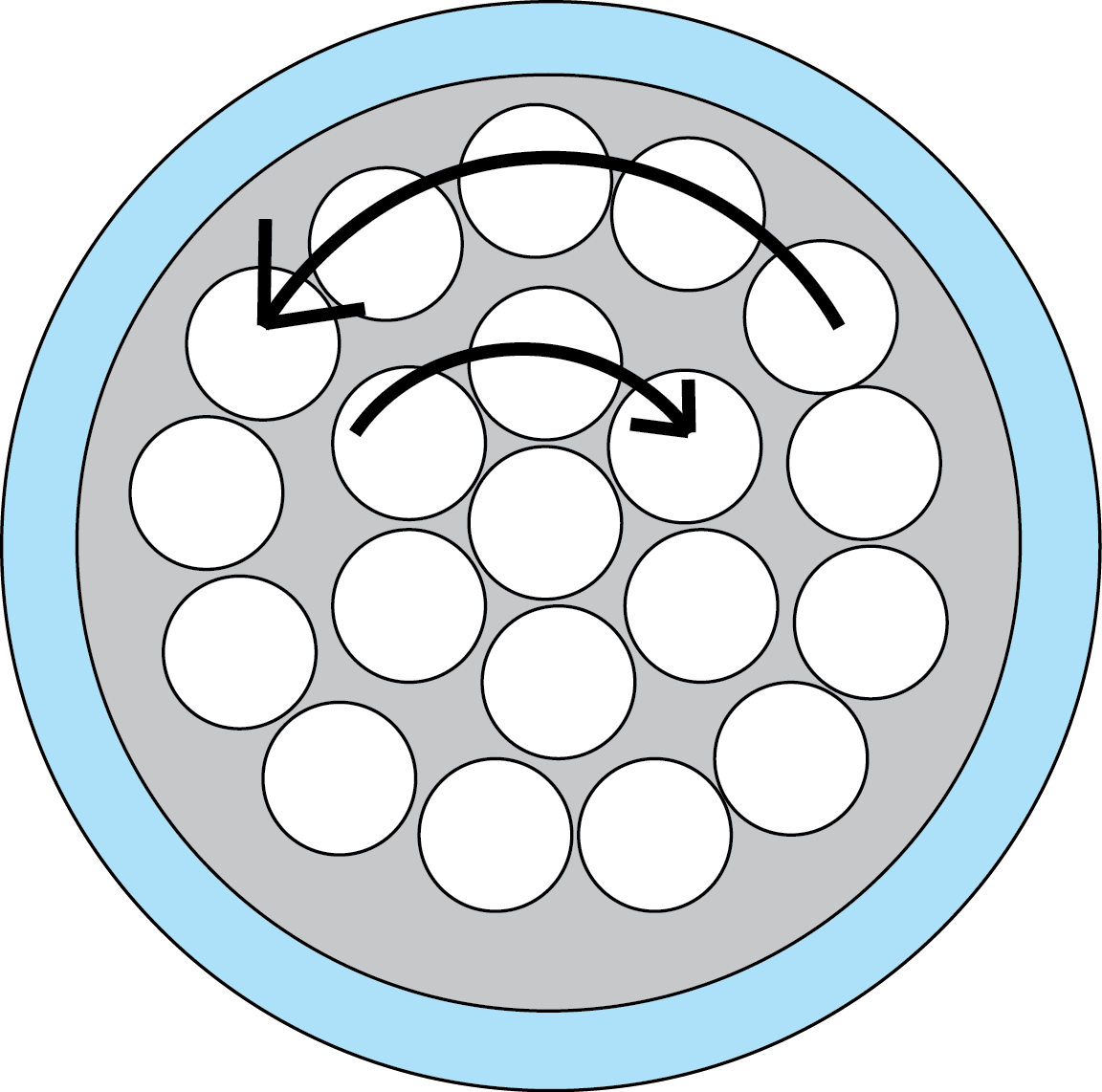
Unilay: has its strands arranged in a circular pattern, with the different layers twisted in the same direction.
 |
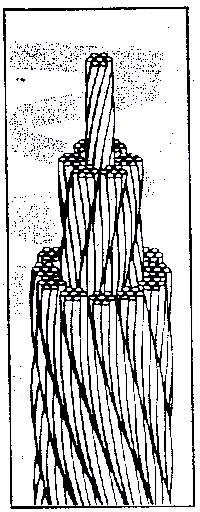 |
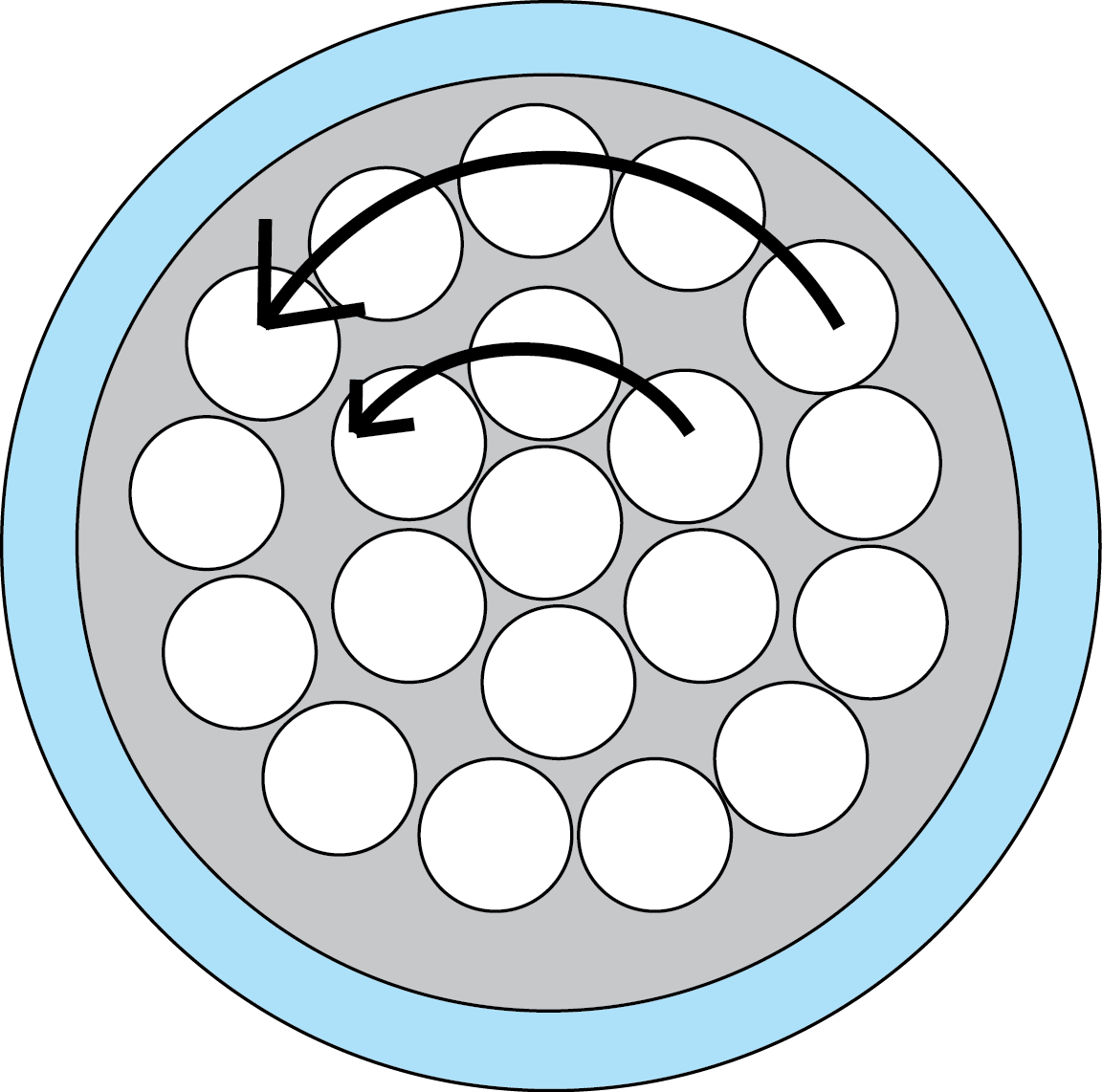
Rope lay: is a concentric lay and has groups of wires laid by on one another in order to form a rope type figure.
2. Insulation & Jacketing
The second major factor to consider when designing a complicated custom cable is insulation and jacketing. Typically insulation and jackets are used as a protective outer layer against any incoming physical abuse like flexing and moisture. There are two popular types of insulation and jackets "Thermoplastic and Thermoset."
Insulation is the first layer, which is in direct contact with the conductor; therefore, the primary job for the insulation of the cable is to stop any leakage (current from escaping). Insulation is also designed to prevent any incoming physical abuse the cable may face during its application. Some of the resistances that different types of cables are able to withstand are high and low temperatures, flames, moisture, chemicals and abrasion. When choosing an insulator, you also have to consider the internal electrical considerations like capacitance, attenuation and voltage rating.
Jacketing is the outer layer of the custom cable and is designed to protect everything inside of it from chemical, moisture and mechanical damage. Jackets similar to insulation come in a range of customizable colours that makes for easy identification and grouping. Being the outer layer characteristics to consider are the flexibility, colour, high and low-temperature flexibility, flame resistance and shelf life per application.
Popular Insulation & Jacketing materials:
- PVC (Polyvinylchloride)
- PE (Polyethylene)
- PUR (Polyurethane)
- TPR/TPE (Thermoplastic rubber/elastomer)
- Thermoplastic CPE (Chlorinated Polyethylene)
- PO (Polyolefin)
3. Shielding
Insulation and jacketing are responsible for not only protecting the cable from the outside; they also have to stop leakage from the inside. Custom cables typically won’t require shielding unless they’re designed for telecommunication applications or are in close proximity to a large number of additional cables. Shielding is designed to protect against interference called EMI (Electromagnetic Interference). EMI can affect your application in several ways, while shielding has a number of ways to protect against it.
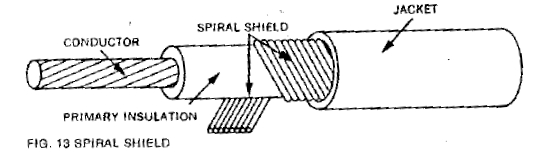
3.1 Spiral: Spiral shields often are created out of a number of different materials, but certain metals like steel may be used for additional physical protection. Spiral shields typically have the highest flexibility and are easily manufactured with 65% overall coverage, while weighing less than most other spirals options.
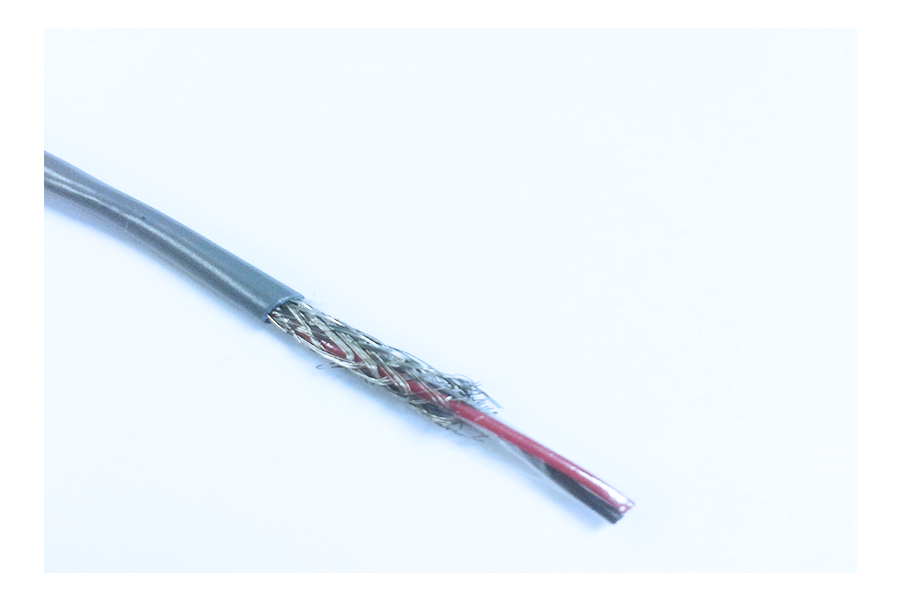
3.2 Braid: The braided shield has moderate flexibility with the material interwoven into a tubular structure or a rectangular cross-section. The braided shield is the oldest form of shielding but is also one of the strongest and most reliable. These braids come in a variety of different material types like steel, aluminum, tinned copper, silver-plated copper & bare copper.
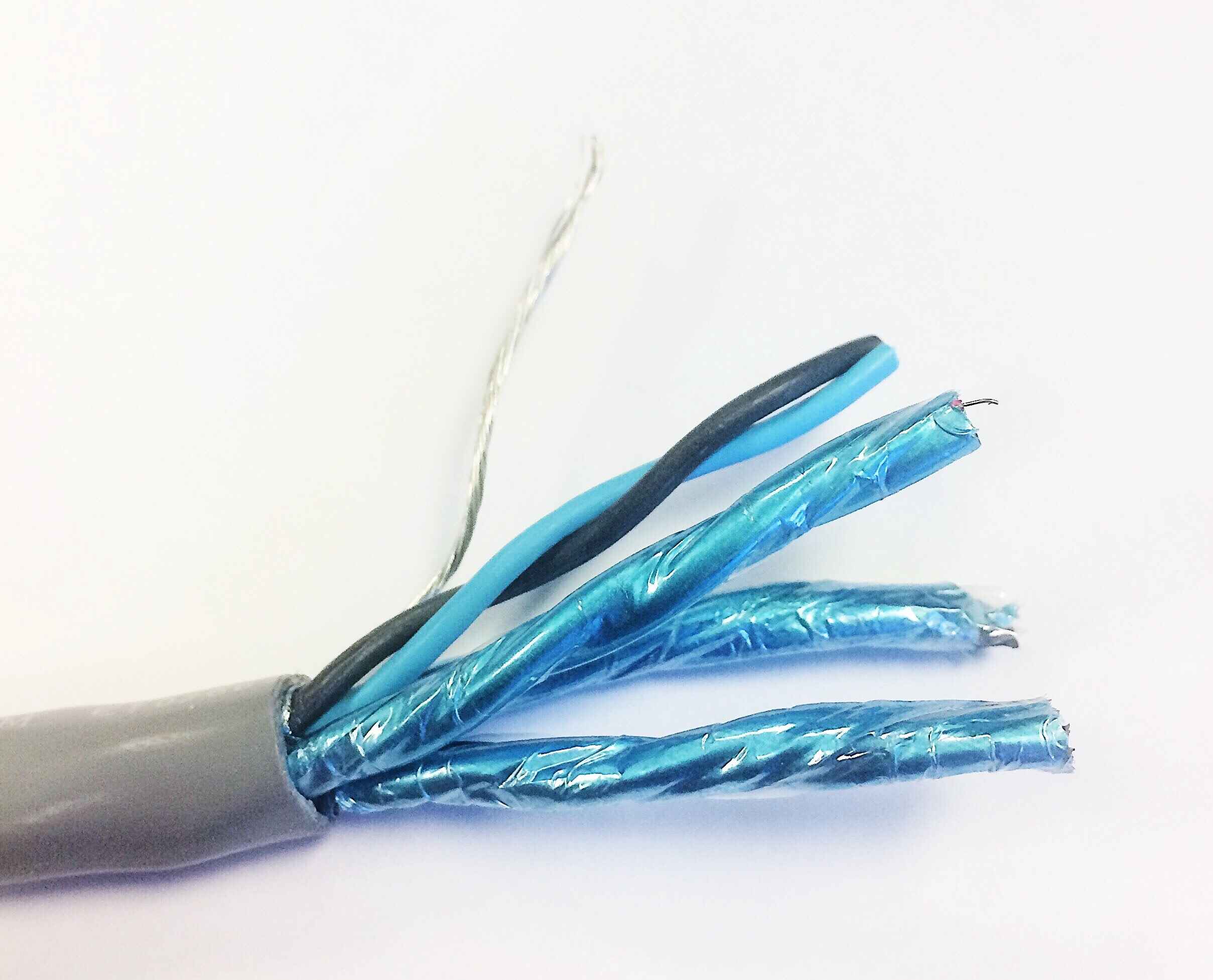

3.3 Foil: Foil shields appear in the shape of a foil gum wrapper and are almost always constructed with tape being either Mylar or Aluminum. Being typically constructed with a drain wire while providing 100% shielding, allows for more effective EMI and noise resistances.
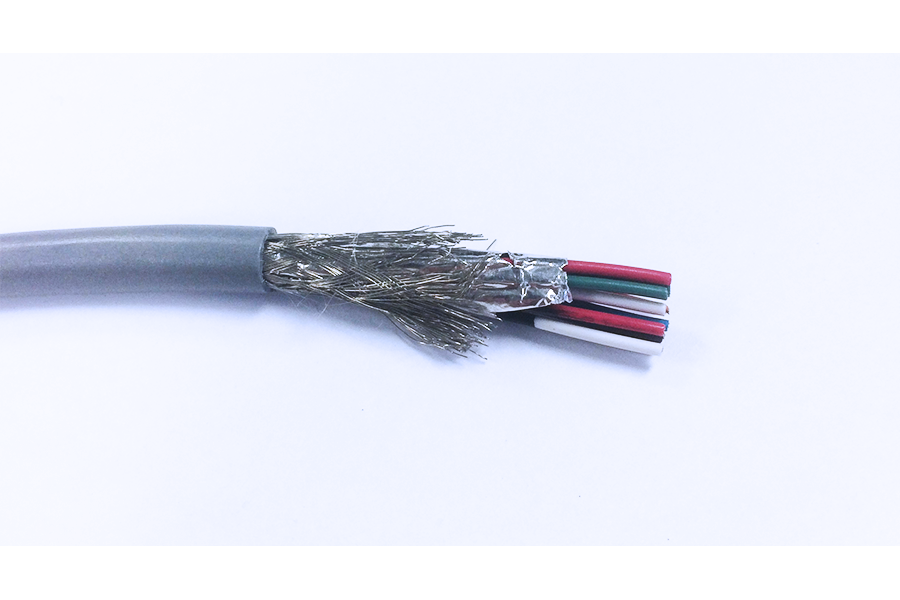
3.4 Combination: This type of shielding is created by combining two or more shields, which are then manufactured into a single cable. The most common type of shielding to combine is the braid over foil or braid over braid. The combination shield is typically used for its 100% foil coverage, mechanical strength, its physical protection, its low DC resistance and flexibility.
4. Fillers
Fillers are relied on for a number of electrical cables, because of how they provide a rounder and smoother construction. Another critical factor to note is electrical fillers help strengthen the cable, so when a cable is moved, it can do so easily. Lastly, fillers support the cables outer layers, while increasing the flexibility of the construction.
Popular Fillers:
- Nylon
- Cotton
- Polypropylene
- Paper
Click here for Sycor Custom cabling page
For more information about us:
Call Toll Free - 1.800.268.9444 or Email Us - [email protected]





