
Breaking down PEEK:
Polyetheretherketone (also known as PEEK) is a relatively new organic thermoplastic, having been discovered in the late 1970s, and then subsequently released into markets in the early 80s by Imperial Chemical Industries. The chemical itself is classed as a semicrystalline thermoplastic, a material with a moderately to highly ordered molecular structure and a sharp melting point. Essentially, this material composition features some level of uniformity throughout, meaning that it has higher structural rigidity than that of an amorphous compound. In addition to this, the sharp melting point means that there will not be much degradation to the shaping of the material up until the point in which it reaches its melting point. Due to these factors, PEEK serves as an excellent option for applications where a strong and resistant substance is required, such as tubing and heat shrink applications in the electrical industry. However, PEEK is not without competition for heat shrink applications, so how does it compare to one of the more common and longer-running choices, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)?
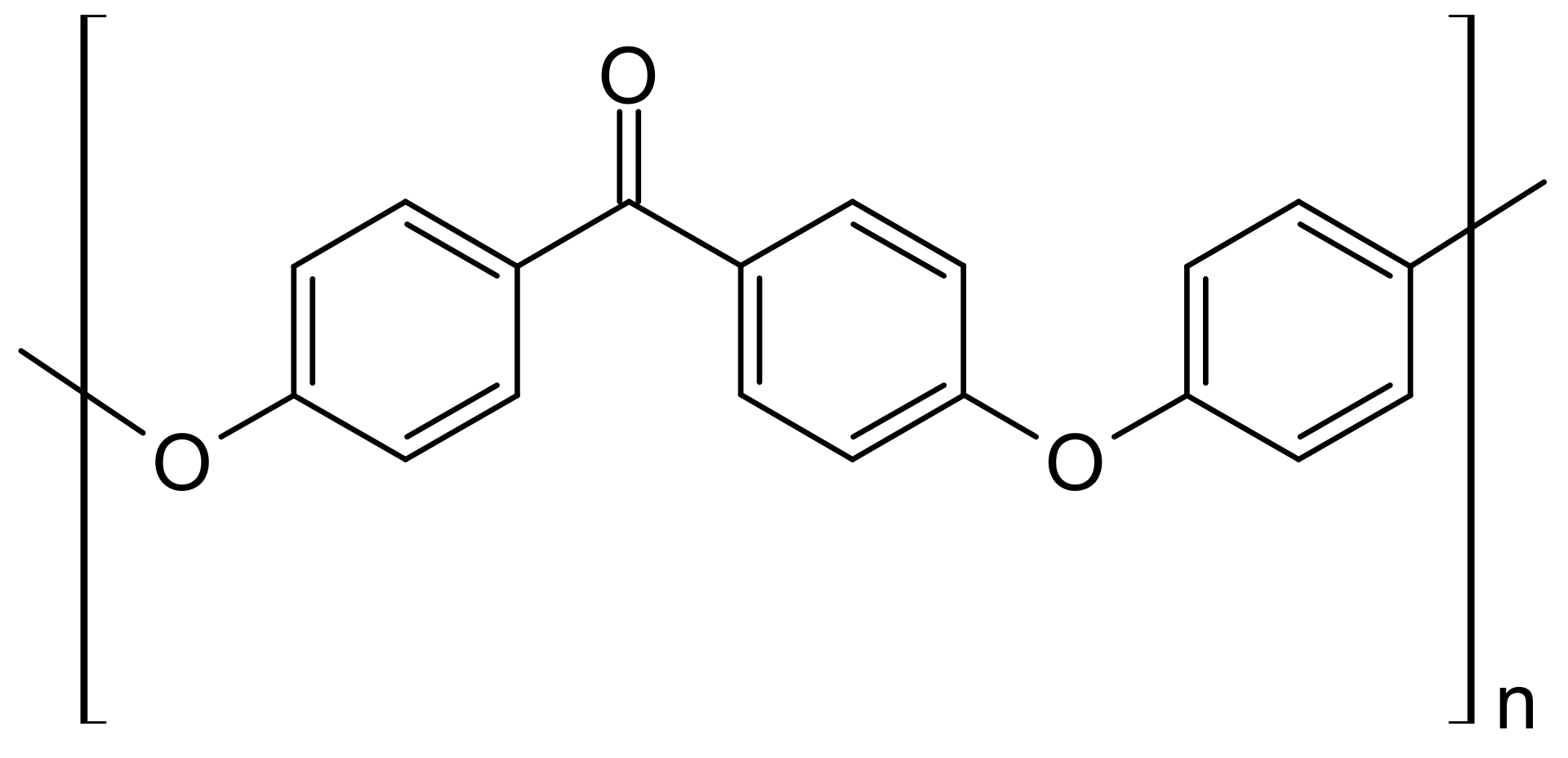
Pictured above is the chemical structure of PEEK
PEEK vs PTFE:
So how do the two options compare to one another? In reality, both have their pros and their cons, depending on the environment in which the product is being used will decide which product is better suited. Listed below is a chart of some parameters used to pit the materials against one another.
|
Parameter |
PTFE |
PEEK |
Preferred Material |
|
Availability |
Common |
Niche |
PTFE |
|
Tensile Strength |
25-35 Mpa |
90-100 Mpa |
PEEK |
|
Elongation |
350-400% |
30-40% |
PTFE |
|
Compressive Strength |
30-40 Mpa |
140 Mpa |
PEEK |
|
Flexural Modulus |
495 Mpa |
3900 Mpa |
PEEK |
|
Coefficient of Friction |
0.03-0.05 |
0.35-0.45 |
PTFE |
|
Operational Temperature Resistance |
Up to 250°C |
Up to 250°C |
NA |
|
Glass Transition Temperature |
115°C |
143°C |
PEEK |
|
Melting Point |
327°C |
343°C |
PEEK |
|
Dielectric strength |
50-150 Kv/mm |
50 Kv/mm |
PTFE |
|
Chemical Resistance |
Virtually inert |
Affected by Sulphuric acid |
PTFE |
|
Damage resistance |
High |
Extreme |
PEEK |
|
Coefficient of linear thermal expansion |
14 x 10-5/K |
5 x 10-5/K |
PEEK |
|
Machine-ability |
Good |
Very good |
PEEK |
|
Price |
Moderately expensive |
Very expensive |
PTFE |
It should also be stated that in real-world applications all these parameters may not necessarily apply. And as such the best option may be the option that checks the most boxes for your application, not which checks the most boxes overall. If you have any questions about which sleeving or tubing product is the right fit for your application, reach out to our sales team at [email protected], you will be connected with an expert who will be able to provide information and the best possible product for your needs.
As shown in the table above, while neither of the two products necessarily falls short in the metrics and tests listed, PEEK does edge out the competition in a majority of the tests making it the overall best possible product for an application. It should be stated that given PEEK’s emerging nature relative to that of PTFE, one could be discouraged from switching over due to its relative scarcity. While this may be a concern for many, this isn’t a concern for Sycor Technology Inc., as over our years in operation we’ve been able to build up relationships with numerous major market suppliers to ensure we have access to an expansive and ever-growing catalog of products for our customers.
Specific use cases of PEEK
Even knowing the areas in which PEEK excels over the competition, one may still be wondering when to use PEEK products. This next portion of the blog will serve as some use cases of these products to provide insight into the optimal times for this line of products:
— In applications where the product will be subject to consistently high temperatures as well as possible material deterioration due to environmental factors. Use in the automotive industry as an example, as PEEK products have a high level of material durability as well as high-temperature resistance, this makes them a prime candidate for such applications where heat and erosion resistance are key.
— Another scenario where PEEK products would serve as the prime option would be in high-stress environments or when protecting delicate components is of the utmost importance. Due to the structural rigidity and material hardness of several forms of PEEK products, they are perfect for any application where metals cannot be used but metal-like durability is still desired. Applications include gaskets, wire and cable encapsulation/insulation, and even medical devices.
— The last of the three prime scenarios for PEEK products would be when the least possible amount of deformation is desired. For products that are regularly being impacted or seeing some form of physical shock regularly—even in scenarios where heat is involved—PEEK boasts higher-than-average stiffness and dimensional stability. Coupled with its high-temperature resistance, PEEK is an ideal solution for applications requiring strengths and low levels of deformation, such as advanced engineering, aerospace, food and beverage, and automotive industries.
While the full list of where PEEK excels is far longer than this, these examples serve as a glimpse into possible solutions for your application. For more information on the different types of sleeving and tubing materials, as well as different types of cable management overall, check out some of our other tubing and sleeving-related materials here.
For more information about us:
Call Toll Free - 1.800.268.9444 or Email Us - [email protected]
Sources:





