The Benefits of Different Wiring Insulations!
Before diving into the wide spectrum of the different chemically formulated insulations, let’s first go over the purpose of electrical insulation. As the name suggests it’s an insulator meaning it keeps things (electricity) within. Wikipedia defines it as "a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely or have very little electric current flow through it under the influence of an electric field (Wikipedia)."
There's a considerable number of wiring insulations, which range from almost identical chemical compounds to being completely different. Many of these similar constructions are basically the same, but certain manufacturers have slightly changed some features of the construction, as it allows them to trademark the material. This makes it increasingly difficult to cover a significant amount of very similar compounds. Therefore, the most efficient way to break down these insulations is by their basic and most popular compound constructions.

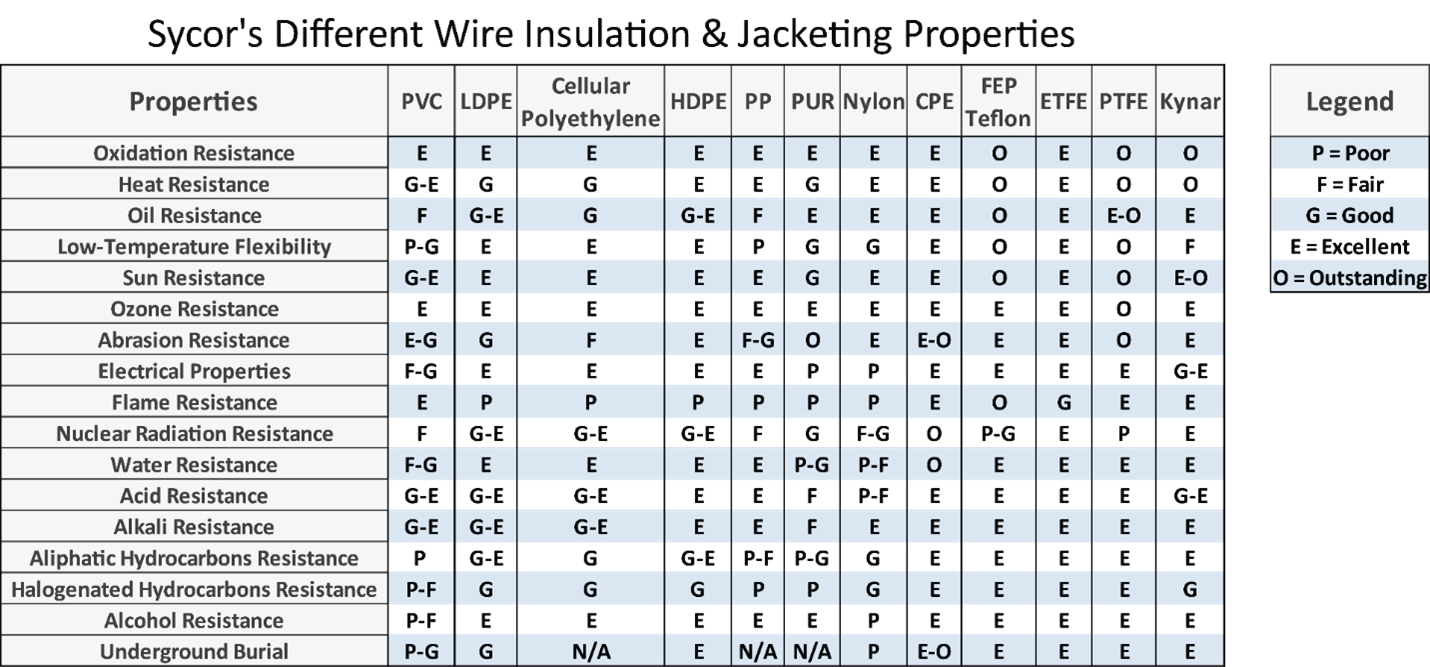
Plastic Wire Insulation
PVC Insulation (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is the third most-produced plastic polymer. PVC is flexible, rigid, and relatively easy to use, while also being one of the most cost-effective choices. The normal temperature range is -55°C to 105°C and is used in applications ranging from medical, food, commercial, and many household applications. Combining PVC with other plasticizers gives the cable additional flexibility and strength, which enables it to be very versatile in difficult application settings.

The most produced plastic in the world because of its versatility in applications and the price that accompanies it. Being a part of the thermoplastic family, PE can continuously be heated and remolded into any shape. Having low dielectric & low captaincies, PE insulation is applicable for a wide range of applications while being resistant to acids, solvents, water, and alkalis.
PP Insulation (Polypropylene)
PP is a thermoplastic polymer that originates from the polyolefin group. Being applicable to a wide range of applications PP is non-polar and has higher heat resistance, a harder outer shell, and less flexibility. PP insulation also has a temperature range of -30°C to 105°C.
PUR Insulation (Polyurethane)
PUR is a polymer that has organic units banded together by carbonate. Being very flexible and tough at low temperatures, PUR isn’t typically used because of its weak electrical properties and its flammability but is still a strong choice with its outer jacket protection.
Nylon Insulation
Nylon has exceptional cut-through, chemical, and abrasion resistance. Nylon is also extremely flexible and typically extruded over softer insulating material. Nylon is a strong alternative for its applications but has weaker moisture penetration, which lowers its overall electrical properties.
Rubber Wire Insulations
TPR Insulation (Thermoplastic Rubber)
TPR is also referred to as thermoplastic Elastomer or TPE. A strong combination of rubber and other plasticizers, this insulation alternative has effective heat, weather, and age resistance. Being a very versatile insulation TPR is a strong choice for harsh, demanding environments.

Neoprene Insulation (Polychloroprene)
Having strong chemical resistance, Neoprene is typically used in Military, Mining, Power, and Oil industries. Neoprene is a strong choice for more difficult harsh applications, as its electrical conductivity does not compare well to other more conductive commercial application alternatives.
Styrene-Butadiene Insulation (SBR)
This synthetic rubber is created from Styrene and Butadiene, which allows it to replace most other natural rubbers. The temperature range of this unique insulation material is -55°C to 90°C. lastly, this material is also abrasion-resistant.
Silicone is a very commonly used general-purpose wiring insulation material. Silicone is also used consistently for high-temperature applications ranging upwards of 150°C or 250°C, depending on what grade you use.
EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber) Insulation
EPR is used for high-voltage applications. Similar to EPDM rubber, this synthetic elastomer has excellent thermal characteristics, with a much smaller cross-sectional area. EPR also has a temperature range of -50°C to 160°C.
Rubber Insulation
This insulation refers to natural rubber, which has a wide range of formulas that can be specifically applied to any application requirements. Rubber is a solid choice as it is very difficult for electricity to break through it, but easy to pass through the insulation passage. This insulation material is also ozone and oil-resistant.
Fluoropolymers Wire Insulations
PFA Insulation
PFA is an electricity-efficient option that can withstand temperatures reaching -100°C to 250°C. PFA is commonly used in Thermocouple wire but is also very effective in Military, Aerospace, Oil, and Gas industry applications. PFA is resistant to fire, chemicals, and UV, as well as good flexibility.
PTFE Insulation (Polytetrafluoroethylene)
PTFE is a very reliable insulator that consistently performs during the application requirements. PTFE is able to withstand -60°C to 200°C temperature range and has fire, UV, and chemical resistance, with excellent flexibility.
FEP Insulation (Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene)
It has excellent electrical properties, a wide temperature range it can be applied to, and is very resistant to chemicals. Having a temperature range of -80°C to 200°C, the FEP insulation can be consistently applied to chemical, aviation, medical, electronics, and aerospace industries.
ETFE Insulation (Ethylene Tetrafluoroethylene)
ETFE is a basic plastic created from fluorine. It is useful in a wide range of applications and has good corrosion resistance, and high strength, with a wide temperature range. This efficient insulation is also recyclable and improves data transmission while reducing the overall weight of the wire.
TPE Insulation (Thermoplastic Elastomers)
TPE has a temperature range of -50°C to 105°C, fire resistance, UV resistance, and reliable flexibility. TPE is typically used in applications requiring Portable control cable, in the medical industry, automotive industry & within robotics. TPE can also be extruded, molded, and reused, all while maintaining the flexibility and other properties of similar rubber insulations.

Fiberglass Insulation
Fiberglass insulations are used in applications involving heat treating, glass and ceramic kilns, foundries, and extensive applications in aluminum processing. Additionally, the insulation is abrasion, chemical, and moisture-resistant.
There's a wide range of many different kinds of insulation, each of which brings potentially different and unique attributes to the conductors they cover. The ability to choose the correct insulation, with the correct wire, for specific applications can be a difficult thing to understand, and even more so if you're inexperienced. Here at Sycor Technology, we understand that not everyone has a full-time career in the wiring industry and may just be purchasing wire for the first time. With our experienced sales, we will be able to narrow down exactly what insulators will best fit the solution you're seeking. Feel free to call or email, and we'd be happy to help answer any questions you may have about insulation material and the wires they protect.
For more information about us:
Call Toll Free - 1.800.268.9444 or Email Us - [email protected]





